Why steam burns are more dangerous than water burns?
Steam burns are more dangerous than water burns because more heat is transferred due to the additional release of latent heat of condensation.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
To vaporize a liquid, energy as heat must be...
Why does water extinguish fire?
By absorbing a very large amount of heat during vaporization, water draws energy from the fire site and thus cools it down until the fire goes out!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
The simple answer to this...
Specific latent heat of solidification (enthalpy of solidification)
Specific heat of solidification is the heat energy to be released for solidification of a liquid per kilogram of the substance!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
Melting and solidification
In the article on specific latent heat of fusion,...
Specific latent heat of fusion (enthalpy of fusion)
The specific latent heat of fusion (enthalpy of fusion) is the amount of heat required to melt a solid substance!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
Process of melting
If a solid is heated more and more, then at...
Specific latent heat of condensation
Specific heat of condensation is the heat energy to be released for condensation of a gas per kilogram of the substance!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
Vaporization and condensation
In the article on specific latent heat of vaporization,...
Specific latent heat of vaporization
The specific latent heat of vaporization (enthalpy of vaporization) is the amount of heat required to vaporize a liquid substance!
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bh43jUpB_F4
Process of vaporization
If a liquid is heated more and more, then at...
Why does the temperature remain constant during a change of state (phase transition)?
During a change of the state of matter, the supplied energy is not used to increase the kinetic energy of the molecules, but to change the binding energies. Therefore, the temperature...
Final temperature of mixtures (Richmann’s law)
Richmann's law of mixtures describes the final temperature resulting in thermodynamic equilibrium when two bodies with different initial temperatures are brought into contact.
https://youtu.be/6tue9N7M1vU
Adiabatic mixing
If two bodies with different initial temperatures are...
Heating and cooling of several objects
Learn more about calculating the final temperature of several objects with different temperatures in this article.
Heating of several objects
In practice, when heating or cooling objects, one usually has to deal with...
Heat capacity of objects
Heat capacity is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of an object by 1 Kelvin (1 °C). Learn more about it in this article.
Specific heat capacity of substances
The...
Calorimeter to determine the specific heat capacities of liquids
Calorimetry deals with the measurement of heat energy.These measurements are based on temperature changes, which are used to determine the amount of heat involved.
Test setup
The experimental setups used in calorimetry are...
Specific heat capacity of gases (at constant volume or pressure)
Due to compressibility of gases, a distinction must be made between the isobaric and the isochoric specific heat capacity.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JZOK2hcQok
Differentiation between isochoric and isobaric heat transfer
Unlike liquids or solids, gases are special...
Specific heat capacity of water
The specific heat capacity of water depends on the temperature and is strongly dependent on the state of matter.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JZOK2hcQok
The specific heat capacity is not a material constant for a substance, but...
Specific heat capacity of selected substances
In this article, learn more about the specific heat capacity of different materials and how it affects the change in temperature over time during a heat transfer.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JZOK2hcQok
Definition of the specific heat...
Important remarks on the specific heat capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JZOK2hcQok
Definition of the specific heat capacity
The specific heat capacity c describes the relationship between a transfer of heat Q and the associated temperature change ΔT of a substance of mass m:
begin{align}label{q}&...
Specific heat capacity (derivation and definition)
The specific heat capacity indicates how much heat must be absorbed by a substance of mass 1 kg in order to increase its temperature by 1 K (1 °C).
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JZOK2hcQok
Introduction
The temperature of...
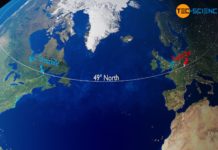
Gulf Stream & global ocean conveyor belt
The Gulf Stream is an ocean current in the Atlantic Ocean which, as part of the earth's global conveyor belt, has a decisive influence on the climate in Northern and Western...
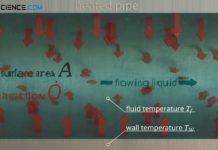
Difference between thermal conductivity, diffusivity, transmittance, resistance and heat transfer coefficient
Learn more in this article about the differences and importance of thermal conductivity, thermal diffusivity, heat transfer coefficient, thermal transmittance and thermal resistance, etc.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity (lambda) describes the heat transfer...
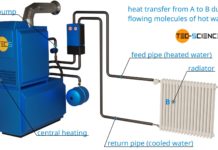
Why are radiators usually located under a window?
Learn in this article, why radiators are usually located under a window?
Central heating systems use the principle of thermal convection. The water is heated by a central heater and then transferred...
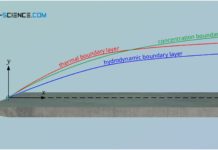
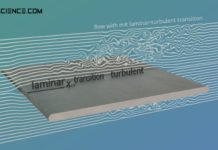
Dimensionless numbers of the boundary layers (Prandtl, Schmidt and Lewis number)
To describe the heat and mass transport, dimensionless numbers are introduced to describe the processes within the boundary layers.
Between a flowing fluid and a solid surface, different boundary layers are formed,...
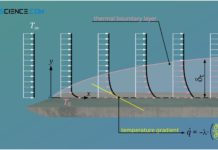
Thermal and concentration boundary layer
In addition to the hydrodynamic boundary layer, the thermal boundary layer and the concentration boundary layer also have a decisive influence on the entire heat and mass transport in a flow.
Temperature...
Prandtl number
The Prandtl number is a dimensionless similarity parameter to describe the transport of heat and momentum.
Definition
In the article on the different boundary layers, the importance of these boundary layers with respect...
Lewis number
The Lewis number is a dimensionless similarity parameter to describe heat and mass transport.
The Lewis number always comes into play when a flowing fluid is transferring both heat by conduction and...
Calculation of the Nusselt numbers for forced flows over plates and in pipes
In this article you will find formulas for calculating the local and average Nusselt numbers for forced flows over plates and in pipes with circular cross sections.
Nusselt number
The definition and importance...
Heat transfer coefficient for thermal convection
The heat transfer coefficient describes the convective heat transfer from a solid to a flowing fluid and vice versa!
Introduction
The heat transfer coefficient describes the convective heat transfer from a solid to...
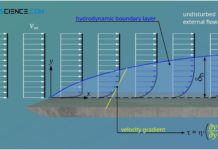
Hydrodynamic boundary layer
The hydrodynamic boundary layer of a flow has a decisive influence on heat and mass transport.
Introduction
In this article we take a closer look at the boundary layers between a solid surface...
Nusselt number to describe convective heat transfer
The Nusselt number is a dimensionless similarity parameter to describe convective heat transfer, independent of the size of the system.
Introduction
Convective heat transfer describes the heat transport between a solid surface and...
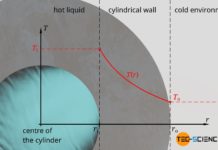
Temperature profiles and heat flows through different geometries
In this article we discuss temperature curves and heat flows through a plane wall, through a cylindrical pipe and through a hollow sphere.
Introduction
Temperature differences cause heat flows. These heat flows, in...
Thermal conduction in solids and ideal gases
The thermal conductivity in crystalline, non-metallic solids first increases and then decreases again with increasing temperature.
Phonons: Quasiparticles of the lattice vibrations
Thermal conduction refers to the transfer of thermal energy through a...
Laser-Flash method for determining thermal conductivity (LFA)
With the Laser-Flash method (Laser Flash Analyser, LFA), the thermal conductivity is determined by the temperature rise in a test sample that is heated by a short laser pulse from one...
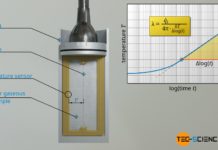
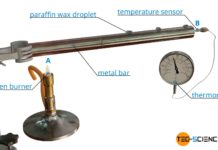
Transient-Hot-Wire method method for determining thermal conductivity (THW)
With the Transient-Hot-Wire method (THW), the thermal conductivity is determined by the change in temperature over time at a certain distance from a heating wire.
Design
With the transient-hot-wire method, the thermal conductivity...
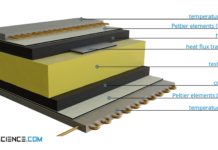
Heat-Flow-Meter method for determining thermal conductivity (HFM)
With the Heat-Flow-Meter method (HFM) the thermal conductivity is determined by comparative measurement of the heat flow using a reference sample.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how well or poorly...
Guarded-Hot-Plate method for determining thermal conductivity (GHP)
With the Guarded-Hot-Plate method (GHP) the thermal conductivity is determined by the electrical power output of a hot plate with guided heat conduction.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how well...
Derivation of heat equation (diffusion equation)
The heat equation describes the temporal and spatial behavior of temperature for heat transport by thermal conduction.
Derivation of the heat equation
We first consider the one-dimensional case of heat conduction. This can...
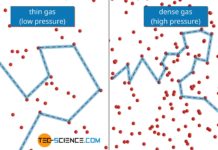
Thermal conductivity of gases
The thermal conductivity of ideal gases is not dependent on pressure for gases that are not too strongly diluted. This is no longer the case for gases with low pressure.
Introduction
In the...
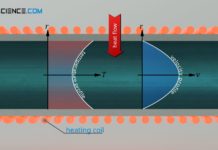
Experimental setup for determining thermal conductivity
In this article you can learn more about the experimental determination of the thermal conductivity of materials using steam and ice.
Thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how well or poorly...
Thermal transmittance (U-value)
The thermal transmittance (U-value or U-factor) describes the heat transfer through a solid object, which is located between two fluids (gas or liquid) with different temperatures.
Definition and unit of the U-value
The...
How does a thermos work? Design of a vacuum flask!
Learn more about the structure of a vacuum flask and how a thermos works in this article!
The reason why hot tea or coffee stays warm for so long in a thermos...
Heat transfer by thermal radiation
With thermal radiation, heat is transferred by electromagnetic waves without the presence of a substance!
The mechanisms of thermal convection and thermal conduction explained in separate articles have one thing in common:...
Heat transfer by thermal convection
With heat transfer by thermal convection, heat is transported with a flowing substance. Convection only occurs in fluids, i.e. gases and liquids.
Introduction
One possibility of heat transfer is that hot substances flow...
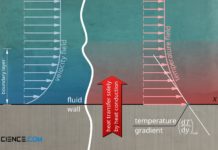
Heat transfer by thermal conduction
Heat transfer by thermal conduction means that heat is conducted through a material. Heat energy is transferred from molecule to molecule at the atomic level.
Introduction
The principle of thermal convection can basically...
Rate of heat flow: Definition and direction
The rate of heat flow refers to the heat energy transferred per unit of time (heat output). The drive for the heat flow is a temperature difference.
Direction of the heat flow
If...
Thermal conductivity (Fourier’s law)
Thermal conductivity is a measure of how well or poorly a material conducts heat energy (measure of the strength of heat conduction)!
Thermal conduction
In general, heat can be transferred in three different...
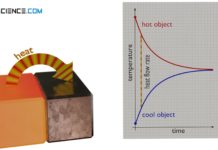
Heat and thermodynamic equilibrium
In thermodynamics, heat is the transport of energy due to a temperature difference. Heat in this respect is never "contained" in an object!
Equalization of temperature of two substances
Everyday experience shows that...
Heat transfer (heat transport)
Heat transfer is the transport of thermal energy from a warmer object to a cooler object. A distinction is made between convection, conduction and radiation.
Example 1: Building
The figure below shows a...
Why does metal feel colder than wood (human thermal response)?
Find out in this article why metal feels colder than wood of the same temperature, while at higher temperatures the metal suddenly feels warmer than wood.
The property of an object to...