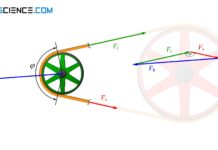
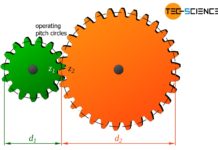
Construction and design of involute gears
Involute toothing is often used in mechanical engineering for gears, as it offers favorable meshing and is easy to produce.
Introduction
In mechanical engineering, the involute...
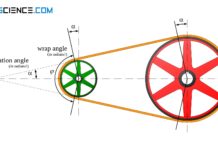
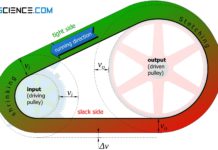
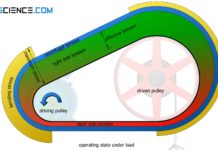
How does a belt drive work?
In belt drives, the power transmission between the driving pulley and the driven pulley is usually force-locked by flexible belts.
Introduction
In belt drives, power is...
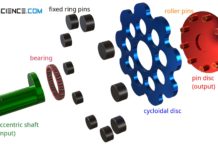
How does a cycloidal drive work?
In this article, you will learn more about the design, the advantages and disadvantages of a cycloidal drive and its application.
Operating principle
The animation below...
Transmission ratios of planetary gears (Willis equation)
Learn more about the derivation of the different transmission ratios of planetary gears in this article.
Willis equation for planetary gears
In the article Willis equation...
Profile shift of involute gears
In the case of a profile shift, the reference profile of the gear is shifted outwards during the manufacturing process in order to positively...
How does a differential gear work?
Learn more about the design, function and application of a differential gear and the differential lock in this article.
Why does a car need a...
Derivation of Willis equation (fundamental equation of planetary gears)
The Willis equation describes the motion of the individual gears of a planetary gearbox (epicyclic gear).
Superposition of motions
The change in speed of planetary gearboxes...
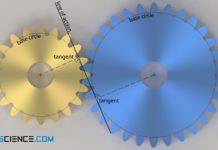
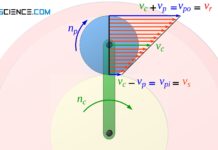
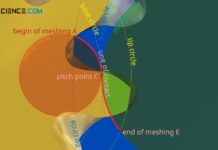
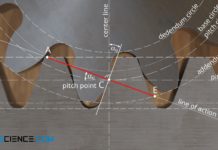
Engaging of involute gears (meshing)
The points of contact of two meshing tooth flanks describe a straight line for involute gears (line of action or line of engagement).
Line of...
Calculation of the belt length for belt drives
Learn in this article how to calculate the length of belts for belt drives.
For the construction of belt drives it is necessary to determine...
Worms and worm gears
With a worm gear, high loads can be transmitted at a high transmission ratio.
Operating principle
A special design of the gear wheel is the so-called...
Slippage of the belt in belt drives
The relative motion on the pulleys, which is always present due to the elasticity of the belt, is called elastic slip!
Elastic slip
When the belt...
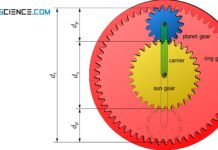
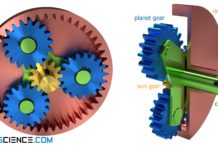
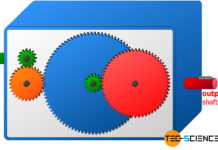
How does a planetary gear work?
A planetary gear is an epicyclic gear in which several gears (planet gears) mesh with a central gear (sun gear).
Stationary gearbox
So-called stationary gearboxes are characterised...
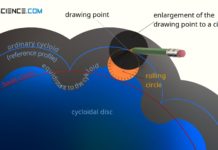
Construction of the cycloidal disc of a cycloidal drive
Learn more about the design of the cycloidal disc of a cycloidal drive in this article.
Design of the cycloidal disc
Cycloidal disc with ordinary cycloid
As...
Overview of gear types
Depending on the shape of the gears and the type of toothing, gears can be classified as spur gears, bevel gears and worms or...
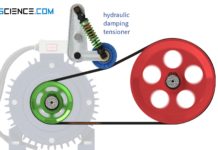
Belt tensioner systems for belt drives
Various belt tensioner systems are used to maintain the tension in the belt. The most important ones are described in more detail below.
Why mus...
Maximum belt stress in belt drives
In this article, learn more about the maximum belt stress, which must not be exceeded, otherwise the belt will be damaged.
Introduction
In general, the forces...
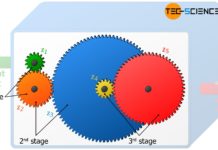
What is a gear stage?
A gear stage is a wheel pairing within a gearbox at which the speed or torque changes! Learn more about gear stages in this...
Willis equation for planetary gears
Learn more about the Willis equation applied to planetary gears in this article.
In the article Derivation of the Willis equation, the fundamental equation for...
Undercut of gears
Undercut occurs when the number of teeth of a gear is too small. An undercut leads to a weakening of the strength of the...
Gear cutting (gear manufacturing)
Learn more about the different manufacturing processes for cutting involute gears in this article.
Gear hobbing
Involute gears are often manufactured by hobbing. The cutting edges...
What is a roots type blower and how does it work?
In this article, learn more about the design and operation of a roots type blower and its application as a supercharger.
Operating principle
The animation below...
Advantages and Disadvantages of belt drives
Learn more about the advantages and disadvantages of belt drives compared to gear drives in this article.
Advantages of belt drives
Compared to a gear drive,...
Calculation of the bearing force for belt drives
Learn more about calculating the bearing force of belt drives at a given preload in this article.
Calculation of bearing force
The forces acting in the...
How does a gearbox (transmission) work?
The conversion of speed and torque takes place in gearboxes through the arrangement of gears or pulleys of different sizes.
Conversion of speed
As explained...
How does a three-speed gear hub work?
Learn more about the structure and function of the planetary gear in a three-speed gear hub in this article.
https://youtu.be/8R3xzAdxYIc
Assembly and function
The figure below schematically...
Meshing of cycloidal gears
In this article, learn more about the meshing of the teeth of cycloidal gears.
Line of action
The figure below shows the meshing of two cycloidal...
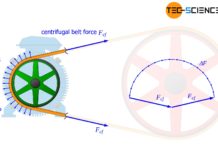
Centrifugal forces in the belt of a belt drive
At high speeds, the centrifugal forces acting on the belt reduce the contact pressure and thus the maximum transmittable circumferential force.
Formation of centrifugal forces
With...
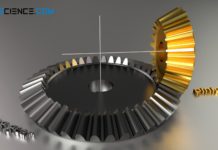
Bevel gears
In bevel gears, the axes of the gears are at right angles to each other. Bevel gears are used to change the spatial direction...
Why do crowned pulleys keep a flat belt on track?
In this article, you will learn why a convex curvature of a crowned pulley will cause a flat belt to keep track and not...
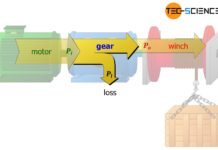
Mechanical power
The mechanical power is determined by the force and speed or by the torque and rotational speed.
Introduction
The term power (in the physical sense) plays an...
Basics of power transmission in belt drives
The basis of power transmission in the belt drive is the belt friction equation according to Euler and Eytelwein (rope friction equation).
Forces acting on...
Screw gears (crossed helical gears)
Screw gears or crossed helical gears are hyperboloid gears that allow the skew mating of the gear shafts!
With the gears considered so far, the...
Lantern pinion as a special case of cycloidal gear
In this article, you can learn more about a lantern pinion as a special case of cycloidal gear.
Operating principle
A special case of cycloidal gearing...
External and internal toothing of gears
With internal toothing, the center distance to an externally toothed gear can be shortened.
For cylindrical gears, a basic distinction can be made between external...
Rack
In this article, learn more about the meshing of the teeth of a gear with the teeth of a rack.
Introduction
The fundamentals when two gears...
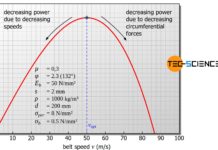
Optimum belt speed for belt drives
At a certain optimum belt speed, a belt drive can transmit the maximum possible power.
Introduction
In the article Mechanical power it was shown that an...
Helical gears
Helical gears have a lower noise level and can transmit higher torques than spur gears!
When it comes down to reduce noises and transmit high...
Spur gears (straight-cut gears)
Straight-cut gears (spur gears) are the simplest type of toothing. In a spur gear, up to 3 teeth are in mesh at the same...
Herringbone gears and double helical gears
Herringbone gears combine the advantage of helical gears (high load capacity) with that of spur gears (no axial forces).
Herringbone gears
In order to combine the...
Hypoid gears (screw bevel gears)
With hypoid gears, rotary motions between non-intersecting axes can be realized!
With the bevel gears considered so far, the axes of the ring gear and...
What is a transmission (gearbox) and what is it used for?
Transmissions control the power supplied in favor of a high velocity (rotational speed) or in favor of a high force (torque)!
Where are gearboxes used?
In...
What types of transmissions (gearboxes) are there?
Roughly speaking, gearboxes are divided into four types: gear drives, belt drives, chain drives and friction wheel drive.
Introduction
Transmission are available in many different types,...
Rack (toothed bar)
Racks (toothed bar) allow the rotary motion of a spur gear to be converted into a straight-line motion of the rack.
While only rotary motions...
Lubrication of gears (transmissions)
Gears must be lubricated due to the high stress (friction) when meshing with another gear.
Introduction
Gear wheels of transmissions are subject to wear due to...