Bohr’s atomic model
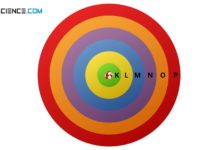
According to the Bohr's atomic model, electrons move on discrete shells around the nucleus (discrete energy levels).
The Rutherford model in many cases provides a very good explanation of physical processes in...
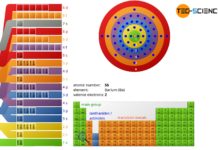
Bohr-Sommerfeld model
The Bohr-Sommerfeld model is an extension of the Bohr model. It explains the distribution of electrons within the shells.
The weaknesses of the Bohr model could be partially eliminated by the physicist...
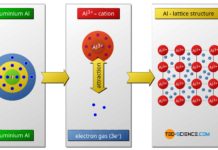
Metallic bonding
In metal bonding, the metal atoms give off their outer electrons and in this way achieve the noble gas configuration.
The main type of bonding between two metals is so-called metal bond. The...
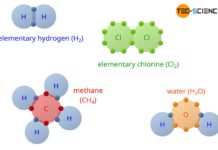
Covalent bonding
In covalent bonding, the atoms involved use shared valence electrons to achieve the noble gas configuration.
The covalent bond mainly occurs between two non-metals. The atoms involved in the bond, share together...
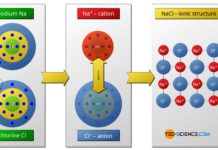
Ionic bonding
In ionic bonding, the metal atoms give off their outer electrons, which are taken up by the non-metal atoms.
The ionic bond is the predominant type of bonding between a metal and...
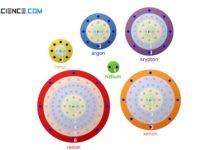
Octet rule
The octet rule refers to the striving of atoms to reach the closest noble gas configuration in the periodic table by forming chemical bonds.
In nature, substances rarely appear as pure elements....